Web 2 (web 2.O) Vs Web 3 (web 3.O) What is the Difference ?
Web2 vs. Web3
Today we’re Going to Discuss Web 2 Vs Web 3 what is the Difference ?
Web2 and Web3 refer to different stages or iterations of the internet and the underlying technologies that power it. Let’s explore the key characteristics and differences between Web2 and Web3:
Web2 (Web 2.0):
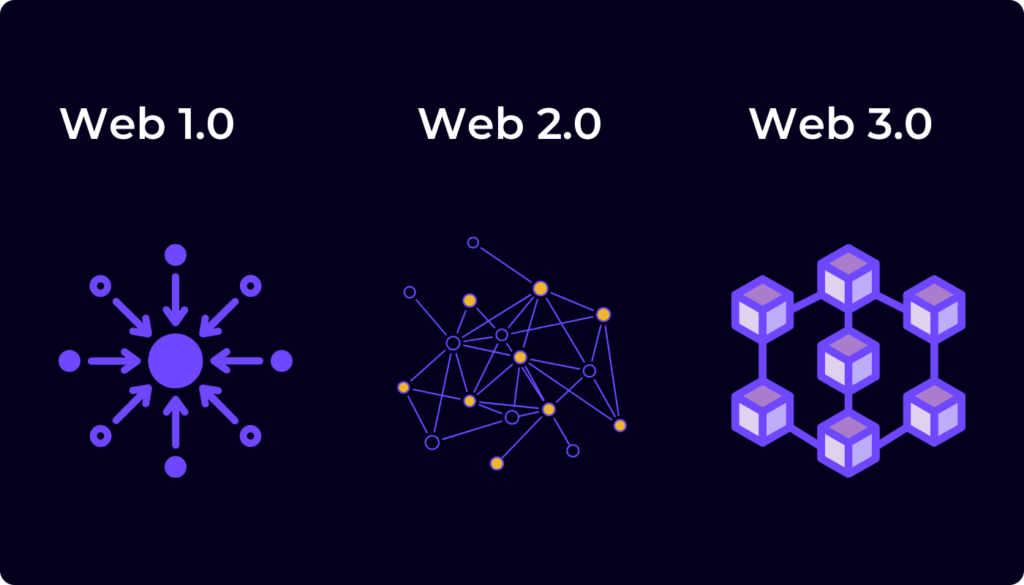
Web2, also known as the second generation of the internet, represents the current state of the internet that emerged in the late 1990s and early 2000s. It is characterized by the following features:
– Centralized Architecture: Web2 relies on centralized servers and infrastructure owned by large corporations or organizations. These entities control the platforms, applications, and data, leading to a concentration of power and control.
– User-Generated Content: Web2 introduced platforms that allowed users to create and share content, leading to the rise of social media, blogging, and video-sharing platforms. Users can interact and collaborate on these platforms but do not have full ownership and control over their data.
– Client-Server Model: Web2 operates on a client-server model where clients (web browsers or applications) request and receive data from centralized servers. The servers store and process data, and the clients display the information to the users.
– Lack of Interoperability: Web2 platforms often operate in isolation, with limited interoperability and data portability between different applications. This restricts the seamless flow and sharing of information across platforms.
Web3 (Web 3.0):
Web3 refers to the vision and development of the next generation of the internet, aiming to address the limitations of Web2. It is centered around the following principles:
– Decentralization: Web3 emphasizes decentralization, shifting away from the concentration of power in the hands of a few entities. It leverages blockchain technology and decentralized protocols to enable peer-to-peer interactions, removing the need for intermediaries and promoting trust and transparency.
– User Control and Data Ownership: Web3 empowers users by giving them ownership and control over their data. Users can decide how their data is shared and accessed, and they can potentially monetize their own data through decentralized platforms.
– Interoperability: Web3 aims to establish interoperability between different platforms and applications. It envisions a connected ecosystem where data and services can seamlessly interact and be shared across various decentralized applications (DApps).
– Smart Contracts and Programmability: Web3 leverages smart contracts, self-executing contracts with predefined rules, to automate transactions and enforce agreements on the blockchain. Smart contracts enable programmability, allowing developers to create decentralized applications with built-in logic and functionality.
– Cryptocurrency and Token Economy: Web3 incorporates cryptocurrencies and token economies, where digital tokens are used for various purposes such as incentivizing participation, governance, and value exchange within the decentralized ecosystem.
– Privacy and Security: Web3 places a strong emphasis on privacy and security, leveraging cryptographic techniques to protect user data and transactions. Users have more control over their identities and can interact with the internet pseudonymously or with privacy-focused measures.
Web3 is an evolving concept, and various projects and protocols are actively working towards its realization. It aims to transform the internet into a more open, decentralized, and user-centric ecosystem, enabling greater privacy, control, and opportunities for individuals and communities.